6.1 KiB
Measured Boot
coreboot measured boot is implemented as Google Verified Boot extension. This means in order to use it, vboot needs to be available for your platform. The goal of this implementation is to implement an easy to understand and transparent measured boot mechanism.
IBB/CRTM
The "Initial Boot Block" or "Core Root of Trust for Measurement" is the first code block loaded at reset vector and measured by a DRTM solution. In case SRTM mode is active, the IBB measures itself before measuring the next code block. In coreboot, cbfs files which are part of the IBB are identified by a metatdata tag. This makes it possible to have platform specific IBB measurements without hardcoding them.
Known Limitations
At the moment measuring IBB dynamically and FMAP partitions are not possible but will be added later to the implementation.
Also SoCs making use of VBOOT_RETURN_FROM_VERSTAGE are not able to use the measured boot extension because of platform constraints.
SRTM Mode
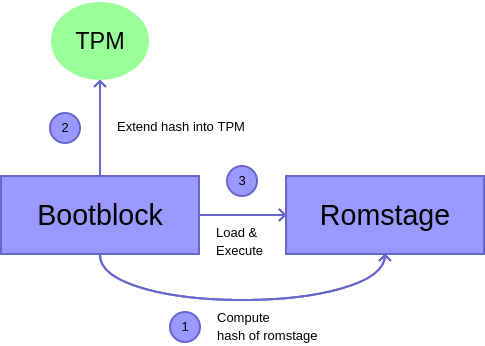
The "Static Root of Trust for Measurement" is the easiest way doing measurements by measuring code before it is loaded.
Measurements
SRTM mode measurements are done starting with the IBB as root of trust. Only CBFS contents are measured at the moment.
CBFS files (stages, blobs)
- CBFS data is measured as raw data before decompression happens.
- CBFS header is excluded from measurements.
- Measurements are stored in PCR 2.
Runtime Data
- CBFS data which changes by external input dynamically. Never stays the same.
- It is identified by VBOOT_MEASURED_BOOT_RUNTIME_DATA kconfig option and measured into a different PCR 3 in order to avoid PCR pre-calculation issues.
TCPA eventlog
coreboot makes use of its own TCPA log implementation. Normally the eventlog specification can be found via the TCG homepage:
Both of them are not representing firmware measurements in a generalized way. Therefore we have to implement our own solution.
We decided to provide an easy to understand TCPA log which can be read out from the operating system and firmware itself.
Table Format
The first column describes the PCR index used for measurement. The second column is the hash of the raw data. The third column contains the hash algorithm used in the operation. The last column provides information about what is measured. First the namespace from where the data came from, CBFS or FMAP, then the name used to look up the data (region or file name).
Example:
PCR-2 e8f2b57c9ec5ea06d1bbd3240a753974d4c3e7c8cd305c20a8ea26eed906dc89 SHA256 [FMAP: COREBOOT CBFS: bootblock]
PCR-2 309a5fcb231d3a39127de2521792f332f9a69e05675ec52535d2dcded756dc19 SHA256 [FMAP: COREBOOT CBFS: fallback/verstage]
PCR-2 0fbba07a833d4dcfc7024eaf313661a0ba8f80a05c6d29b8801c612e10e60dee SHA256 [FMAP: RO_VPD]
PCR-2 431681113ed44cbf6f68a12c6e5687e901052f1d728a4777b2ad36e559962047 SHA256 [FMAP: GBB]
PCR-2 f47a8ec3e9aff2318d896942282ad4fe37d6391c82914f54a5da8a37de1300c6 SHA256 [FMAP: SI_DESC]
PCR-3 237f6f567f8597dbdff0a00690d34d21616af0dbe434b9a2d432b136c012765f SHA256 [FMAP: SI_ME]
PCR-2 7d2c7ac4888bfd75cd5f56e8d61f69595121183afc81556c876732fd3782c62f SHA256 [FMAP: SI_GBE]
PCR-0 62571891215b4efc1ceab744ce59dd0b66ea6f73 SHA1 [GBB flags]
PCR-1 a66c8c2cda246d332d0c2025b6266e1e23c89410051002f46bfad1c9265f43d0 SHA256 [GBB HWID]
PCR-2 ceca357524caf8fc73f5fa130f05a75293031962af884e18990d281eb259f5ff SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: fallback/romstage]
PCR-2 548a097604e0a975de76f98b04c7f0b0ddec03883dd69179e47a784704a1c571 SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: fspm.bin]
PCR-2 1e86b27008818244c221df2436b0113bd20a86ec6ec9d8259defe87f45d2f604 SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: spd2.bin]
PCR-2 05d78005fcfc9edd4ca5625f11b1f49991d17bdb7cee33b72e722bc785db55ae SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: fallback/postcar]
PCR-2 c13e95829af12a584046f1a6f3e1f6e4af691209324cfeeec573633399384141 SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: fallback/ramstage]
PCR-2 a6ec2761b597abd252dba2a7237140ef4a5a8e0d47cad8afb65fa16314413401 SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: cpu_microcode_blob.bin]
PCR-2 c81ffa40df0b6cd6cfde4f476d452a1f6f2217bc96a3b98a4fa4a037ee7039cf SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: fsps.bin]
PCR-2 4e95f57bbf3c6627eb1c72be9c48df3aaa8e6da4f5f63d85e554cf6803505609 SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: vbt.bin]
PCR-3 b7663f611ecf8637a59d72f623ae92a456c30377d4175e96021c85362f0323c8 SHA256 [FMAP: RW_NVRAM]
PCR-2 178561f046e2adbc621b12b47d65be82756128e2a1fe5116b53ef3637da700e8 SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: fallback/dsdt.aml]
PCR-2 091706f5fce3eb123dd9b96c15a9dcc459a694f5e5a86e7bf6064b819a8575c7 SHA256 [FMAP: FW_MAIN_B CBFS: fallback/payload]
Dump TCPA eventlog in the OS:
cbmem -L
Get CBFS file and print the hash
cbfstool coreboot.rom extract -r COREBOOT -n fallback/romstage -U -f /dev/stdout | sha256sum
Get FMAP partition and print the hash
cbfstool coreboot.rom read -n SI_ME -f /dev/stdout | sha256sum
DRTM Mode
The "Dynamic Root of Trust for Measurement" is realised by platform features like Intel TXT or Boot Guard. The features provide a way of loading a signed "Authenticated Code Module" aka signed blob. Most of these features are also a "Trusted Execution Environment", e.g. Intel TXT.
DRTM gives you the ability of measuring the IBB from a higher Root of Trust instead of doing it yourself without any hardware support.
Platform Configuration Register
Normally PCR 0-7 are reserved for firmware usage. In coreboot we use just 4 PCR banks in order to store the measurements. coreboot uses the SHA-1 or SHA-256 hash algorithm depending on the TPM specification for measurements. PCR-4 to PCR-7 are left empty.
PCR-0
Hash: SHA1
Description: Google VBoot GBB flags.
PCR-1
Hash: SHA1/SHA256
Description: Google VBoot GBB HWID.
PCR-2
Hash: SHA1/SHA256
Description: Core Root of Trust for Measurement which includes all stages, data and blobs.
PCR-3
Hash: SHA1/SHA256
Description: Runtime data like hwinfo.hex or MRC cache.